
INCOTERMS
Incoterms is the contraction of “International Commercial Terms” and constitutes a codified set of standard contractual provisions relating to the carriage of goods. The Incoterm is essential for planning any international shipment, and is always associated with a geographical location that represents the “critical point” at which responsibility is transferred between the seller and the buyer. The latest version dates from 2020, and they are revised every ten years to reflect changes in international trade practices.
An Incoterm is not a contract of sale, but it does bind the seller to a buyer.
THE ROLE OF INCOTERMS
Incoterms are designed to share international logistics costs and risks between seller and buyer. Each incoterm mainly offers:
- The division of international logistics operations and the corresponding costs between the seller and the buyer
- The obligations of the seller and the buyer
- The point at which the risk in the goods passes from the seller to the buyer
- Documentary obligations
However, these rules do not govern:
- Transfer of ownership
- Method of payment
- Applicable law
- Jurisdiction
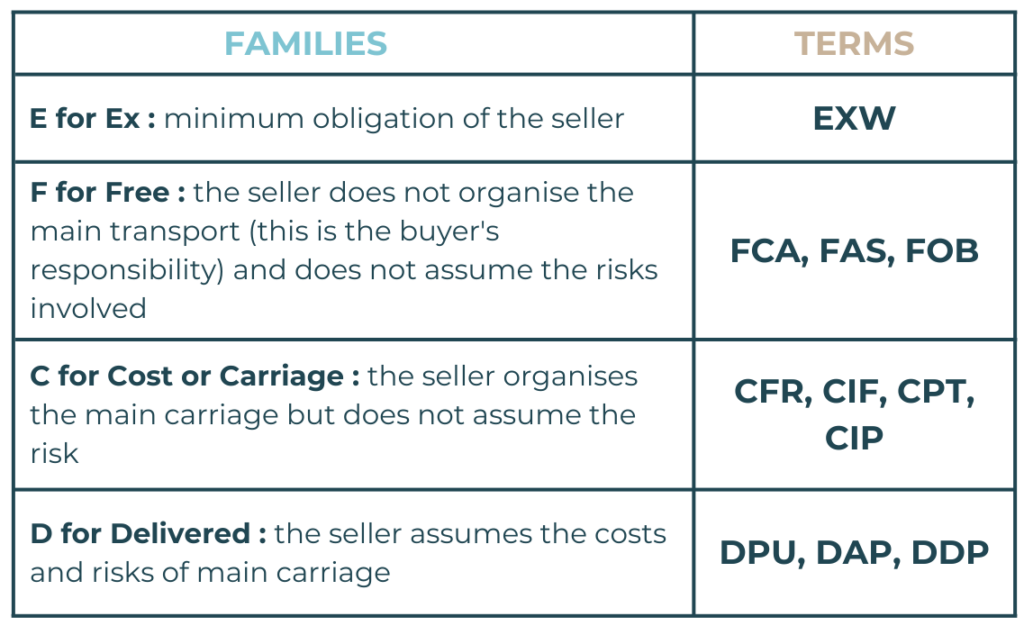
4 GROUPS OF INCOTERMS
There are several families of Incoterms:
2 TYPES OF INCOTERMS
These 4 groups of Incoterms are divided into two categories of Incoterms used according to the mode of transport chosen.
Multimodal Incoterms:
Suitable for all international modes of transport: sea, air, rail and road. These Incoterms are intended for use when the place where the seller hands over the goods to the buyer is not on board a ship or in a sea or river port.
- EXW: Ex Works (ex works)
- FCA: Free Carrier
- CPT: Carriage Paid To
- CIP: Carriage and Insurance Paid To
- DAP: Delivered At Place
- DPU: Delivered at Place Unloaded
- DDP: Delivered Duty Paid
Maritime Incoterms:
The 4 Incoterms are called “maritime” because they are intended to be used when the seller places the goods on board or in the vicinity (in the case of FAS) of a ship, in a sea or river port.
- FAS: Free Alongside Ship
- FOB: Free On Board
- CFR: Cost and Freight
- CIF: Cost Insurance and Freight
TRANSPORT INSURANCE AND INCOTERMS
With the exception of CIP and CIF, where insurance is required, it is not compulsory for the other incoterms, but is strongly recommended.
- For CIPs, the insurance required is “all risks”.
- For CIFs, the minimum insurance required is “FAP except”.
CHOICE OF INCOTERM
1/ Depending on the goods
If the customer is exporting sensitive or high value-added goods such as frozen food or luxury goods, we recommend mastering the entire transport chain in order to choose the most appropriate means of transport.
2/ Depending on the country of destination
The more complex and numerous the formalities in the importing country, the more complicated it is for an exporting company to manage transport and its obligations. So it’s best to let the importer take charge from the moment the goods are loaded through to shipment.
Contact us to find out more about incoterms and how to choose them, or to receive our detailed flyer.








